Introducción a Interfaz gráfica (GUI)
El paquete tkinter (Tk interface) es una interface estándar de Python para el toolkit Tcl/Tk GUI (Interfaz Gráfica de Usuario). Ambos Tk y tkinter esta disponible en la mayoría de las plataformas Unix, incluida macOS, como también en sistemas Windows.
Tkinter no es un wrapper, pero agregar un poco de su propia logia haciendo la experiencia mas pythonica.
Iniciando con Tkinter
Para importar el modulo tkinter, es decir, es decir para poder generar una ventana inicial o principal y para importar o generar widgets se importa el modulo ttk:
from tkinter import *
from tkinter import ttk
El modulo Tk incluye soporte para los siguientes módulos:
- tkinter
-
Modulo principal
-
Ventana dialogo que le permite al usuario elegir un color.
-
Clase base para un ventana de dialogo en otro modulo
-
Ventana de dialogo común que permite al usuario especificar guardar o abrir un archivo.
-
Utilidades que te ayudan a trabajar con fuentes (Fonts)
-
Acceder a ventanas de dialogo estándar.
-
Crea un scroll vertical a los Widget tipo texto.
-
Ventana de dialogo básica y funciones convenientes a ello.
- Es un set de widgets introducidos en
Tk8.5, provee una alternativa moderna de muchos widgets clásicos en el modulo principal tkinter
Tk - Ventana principal
Cuando desarrollamos una aplicación GUI se necesita una ventana principal, la cual va a contener todos los elementos (widget) dentro de la misma; es decir, botones, etiquetas (Texto), cajas de texto, cajas para marcar (checkbox, radiobutton), frames (ventanas), etc. Inclusive la propia ventana (Tk) principal es un widget. Dentro de las ventanas se colocan los widgets
Important Tk Concepts
Even this simple program illustrates the following key Tk concepts:
Widgets
A Tkinter user interface is made up of individual widgets. Each widget is represented as a Python object, instantiated from classes like ttk.Frame, ttk.Label, and ttk.Button.

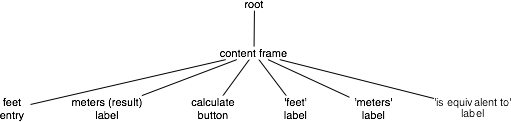
Widget hierarchy
Widgets are arranged in a hierarchy. The label and button were contained within a frame, which in turn was contained within the root window. When creating each child widget, its parent widget is passed as the first argument to the widget constructor.
configuration options
Widgets have configuration options, which modify their appearance and behavior, such as the text to display in a label or button. Different classes of widgets will have different sets of options.
geometry management
Widgets aren’t automatically added to the user interface when they are created. A geometry manager like grid controls where in the user interface they are placed.

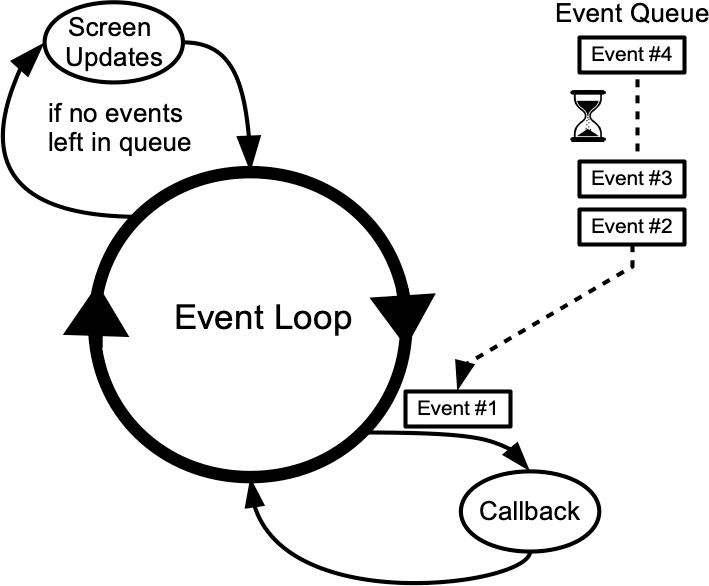
event loop
Tkinter reacts to user input, changes from your program, and even refreshes the display only when actively running an event loop. If your program isn’t running the event loop, your user interface won’t update.